Discover the health benefits and risks of caffeine. Learn how caffeine affects your body, safe daily intake, and its impact on energy, focus, and wellness.
Introduction
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances in the world. Found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks, it has become a daily ritual for millions seeking increased alertness and productivity. But while caffeine has many health benefits, overconsumption may lead to negative side effects. This article explores what caffeine is, how it works in the body, its health benefits, potential risks, and recommended intake levels.
What is Caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant most commonly found in coffee beans, tea leaves, cacao pods, and kola nuts. It works by stimulating the central nervous system, temporarily warding off drowsiness and restoring alertness. As a result, caffeine is often used to boost energy, enhance focus, and improve physical performance.
How Caffeine Works in the Body
When consumed, caffeine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain. It blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation, which leads to increased alertness. Additionally, caffeine increases the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, chemicals that improve mood, focus, and reaction time.
Health Benefits of Caffeine
1. Boosts Mental Alertness
Caffeine enhances concentration, attention span, and reaction times, making it especially beneficial for tasks requiring focus and quick decision-making.
2. Improves Physical Performance
Studies show that caffeine can improve endurance, strength, and athletic performance by increasing adrenaline levels and breaking down body fat for fuel.
3. Supports Weight Management
Caffeine has mild thermogenic properties, meaning it can slightly increase metabolism and fat burning. This makes it a common ingredient in weight-loss supplements.
4. Provides Antioxidants
Coffee and tea, major sources of caffeine, are also rich in antioxidants that help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
5. May Lower Risk of Certain Diseases
Research suggests moderate caffeine consumption may reduce the risk of conditions like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
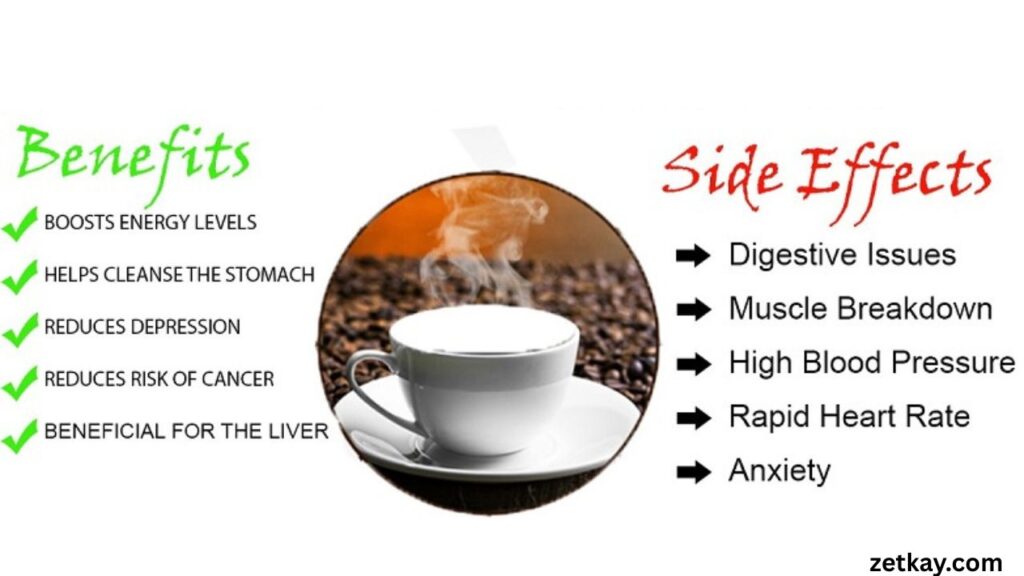
Risks and Side Effects of Caffeine
1. Sleep Disturbances
Consuming caffeine late in the day can interfere with sleep, leading to insomnia or poor sleep quality.
2. Anxiety and Jitters
High doses of caffeine can overstimulate the nervous system, leading to restlessness, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
3. Digestive Issues
Some people may experience stomach discomfort or acid reflux after consuming caffeinated drinks.
4. Dependence and Withdrawal
Regular caffeine consumption can lead to dependency. Symptoms of withdrawal include headaches, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Safe Daily Caffeine Intake
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), most healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day about 4–5 cups of coffee. Pregnant women and individuals with certain health conditions should limit intake to lower amounts.
Sources of Caffeine
- Coffee: 95 mg per 8 oz cup
- Tea: 30–70 mg per 8 oz cup
- Energy drinks: 70–200 mg per serving
- Dark chocolate: 20–30 mg per ounce
- Medications: Some pain relievers and supplements also contain caffeine.
Tips for Healthy Caffeine Consumption
- Stick to moderate amounts (200–400 mg per day).
- Avoid caffeine at least 6 hours before bedtime.
- Balance caffeine with hydration, since it has mild diuretic effects.
- Choose natural sources like coffee and tea over heavily processed energy drinks.
Conclusion
Caffeine can be a powerful tool for enhancing mental alertness, physical performance, and even long-term health when consumed in moderation. However, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as anxiety, poor sleep, and dependency. The key is finding the right balance that works for your body and lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is caffeine bad for your heart?
Moderate caffeine intake is generally safe for healthy individuals. However, people with heart conditions should consult their doctor before consuming large amounts.
2. How long does caffeine stay in your system?
Caffeine’s half-life is about 5–6 hours, meaning it takes that long for half of it to leave your system.
3. Can caffeine help with headaches?
Yes, caffeine can reduce headache symptoms by narrowing blood vessels, which is why it is included in some pain medications.
4. Is caffeine safe during pregnancy?
Pregnant women are advised to limit caffeine intake to less than 200 mg per day.
5. What is the healthiest source of caffeine?
Natural sources like coffee and tea provide caffeine along with antioxidants and other beneficial compounds.
