Learn about adult pneumonia symptoms, causes, and risk factors. Discover the warning signs like cough, fever, chest pain, and shortness of breath to know when to seek medical help.
Introduction
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can range from mild to life-threatening. It happens when germs like bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter the lungs and cause inflammation. Pneumonia can be especially dangerous for adults because symptoms are sometimes ignored or mistaken for a common cold or flu. Understanding the signs and risk factors allows you to take action early and prevent serious complications. In this article, we will explore the main symptoms of adult pneumonia, what causes it, and how you can protect yourself.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that affects the air sacs inside the lungs. These tiny sacs, called alveoli, usually fill with air when we breathe. But in pneumonia, they become filled with fluid or pus, making it hard for oxygen to enter the blood. This leads to coughing, fever, chest pain, and breathing problems. Pneumonia can affect just one lung or both lungs at the same time. Adults of all ages can get pneumonia, but it is more dangerous for older people and those with weak immune systems.
Common Adult Pneumonia Symptoms
Recognizing pneumonia symptoms in adults is very important for early treatment. The signs may start suddenly or develop slowly, and they can be mild or severe depending on your overall health. Adults usually experience a combination of symptoms that affect their breathing, energy, and general well-being. Proper treatment can prevent the illness from worsening if these signs are noticed early.
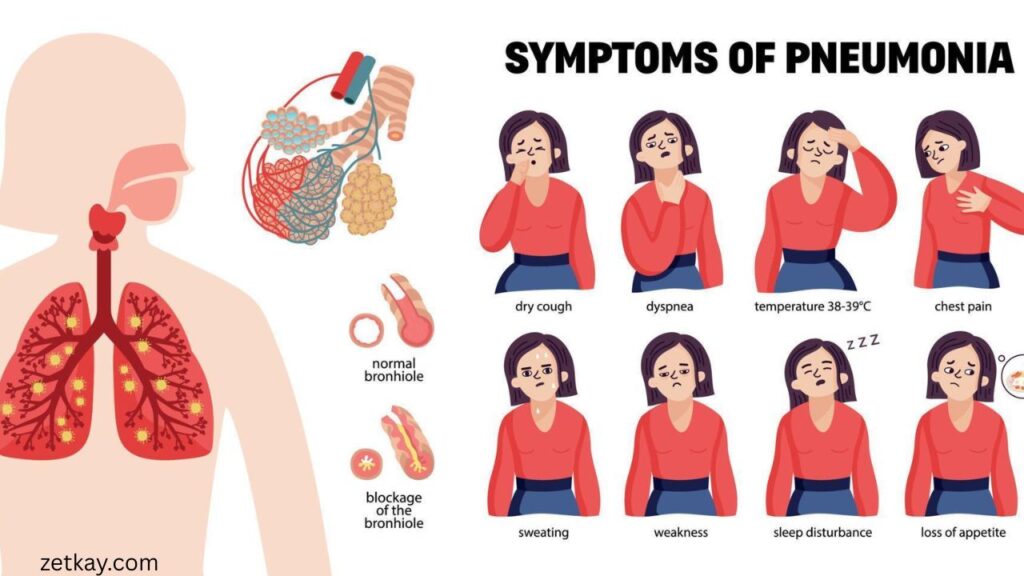
Cough with Mucus
A persistent cough is one of the first and most common symptoms of pneumonia in adults. Unlike a regular cough, this one usually produces thick mucus or phlegm. The mucus can appear green, yellow, or sometimes even blood-streaked. This happens because the lungs are fighting infection. A cough with mucus indicates that your body is struggling with something more serious than a cold.
Fever and Chills
Another significant symptom of pneumonia is a sudden rise in body temperature. Many adults with pneumonia experience high fever, shaking chills, and sweating. The fever may appear quickly and is often higher than what you get with a common flu. These signs show that the body is trying to fight the infection, but also signal that medical attention may be needed.
Shortness of Breath
Adults with pneumonia often complain of shortness of breath. Simple activities like walking to the bathroom or climbing stairs may leave you feeling breathless. This happens because the lungs cannot breathe enough oxygen due to fluid or pus in the air sacs. Shortness of breath is a warning sign that should never be ignored, especially if it happens suddenly.
Chest Pain
Chest pain is another common symptom of pneumonia in adults. The pain usually feels sharp or stabbing and worsens when you take deep breaths or cough. Many people mistake this pain for heart problems or muscle strain, but it is often linked to a lung infection. Chest pain with coughing and fever is a strong sign that pneumonia may be present.
Fatigue and Weakness
Pneumonia drains the body of energy. Adults who develop pneumonia often feel extremely weak and tired, even when they have done very little. This fatigue can last long after other symptoms improve and may affect daily activities such as working, cooking, or even getting out of bed. Ongoing weakness signals that the body is struggling to fight the infection.
Confusion in Older Adults
For older adults, pneumonia may not show in the usual way. Instead of coughing and fever, elderly patients may experience sudden confusion, memory loss, or changes in mental awareness. This symptom is often missed or confused with age-related problems, but it can be a sign of severe lung infection. Families and caregivers should always consider sudden confusion a red flag for pneumonia.
Causes of Pneumonia in Adults
Several different germs can cause pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia is the most common type in adults and often starts after a cold or flu. Viral pneumonia is usually linked to viruses like influenza, RSV, or COVID-19. Fungal pneumonia is less common but can affect adults with weak immune systems or chronic health conditions. Adults who smoke, drink too much alcohol, or live in polluted environments are also at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Risk Factors for Adults
Not all adults face the same risk of pneumonia. People over the age of 65 are much more likely to develop severe pneumonia compared to younger adults. Smokers damage their lungs, making it easier for infections to enter. Adults with chronic diseases like asthma, diabetes, or heart disease are also at higher risk. A weak immune system caused by certain medicines or illnesses can increase the chances of pneumonia. Understanding these risk factors helps adults take preventive steps to stay safe.
Complications of Pneumonia
If pneumonia is not treated in time, it can cause dangerous complications. One complication is a lung abscess, a pocket of pus inside the lung. Another is pleural effusion, where fluid builds up around the lungs, making breathing even harder. In severe cases, bacteria from the infection can enter the blood, leading to a life-threatening condition called bacteremia. Respiratory failure, where the lungs cannot provide enough oxygen, is another serious complication. These dangers show why it is essential to seek medical care quickly.
When to See a Doctor
You should not wait too long if you suspect pneumonia. Adults must see a doctor immediately if they experience high fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, or confusion. If a cough with mucus lasts over a week and does not improve with rest, it is also time to get checked. Early medical attention can prevent hospitalization and reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention Tips for Adults
The good news is that pneumonia can often be prevented. Vaccines for flu and pneumonia are strongly recommended for adults, especially those over 65 or with chronic health problems. Good hygiene, like washing hands regularly and covering your mouth when coughing, also lowers the risk of infection. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to protect your lungs. A healthy diet, enough sleep, and regular exercise all help the immune system fight infections more effectively.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious illness that adults should never ignore. By understanding adult pneumonia symptoms such as cough with mucus, fever, chest pain, and shortness of breath, you can recognize the illness early and seek medical help. Older adults and people with health conditions are especially at risk, so prevention and quick action are significant. If you or someone you know shows signs of pneumonia, do not wait get medical care immediately. Acting early can save lives and prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Adult Pneumonia
1. What are the first signs of pneumonia in adults?
The first signs often include a persistent cough with mucus, fever, and chest discomfort. Some adults may also feel tired, weak, and short of breath. In older adults, confusion or sudden changes in mental awareness can be the first symptom.
2. Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, some types of pneumonia are contagious, especially those caused by bacteria and viruses. Pneumonia can spread through coughing, sneezing, or contact with an infected person. Good hygiene and avoiding contact with sick individuals can help reduce the risk.
3. How long does pneumonia last in adults?
The recovery time depends on the severity of the infection and overall health. Mild pneumonia may improve within 1 to 2 weeks, while more serious cases can take months or longer. Fatigue and weakness may continue even after other symptoms improve.
4. What causes pneumonia in adults?
Bacteria, viruses, or fungi usually cause pneumonia in adults. The most common cause is bacterial pneumonia, often after a cold or flu. Risk factors such as smoking, weakened immunity, and chronic health problems make adults more likely to develop pneumonia.
5. Can pneumonia go away on its own?
Mild viral pneumonia may improve without antibiotics, but bacterial pneumonia usually needs medical treatment. Without proper care, pneumonia can become severe and lead to complications. It is always safest to see a doctor if you suspect pneumonia.
6. What should adults eat during pneumonia recovery?
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains helps the body recover faster. Drinking plenty of fluids, like water and warm soups, also helps thin mucus and keep the lungs clear. Avoiding alcohol and smoking is essential for faster healing.
